Description
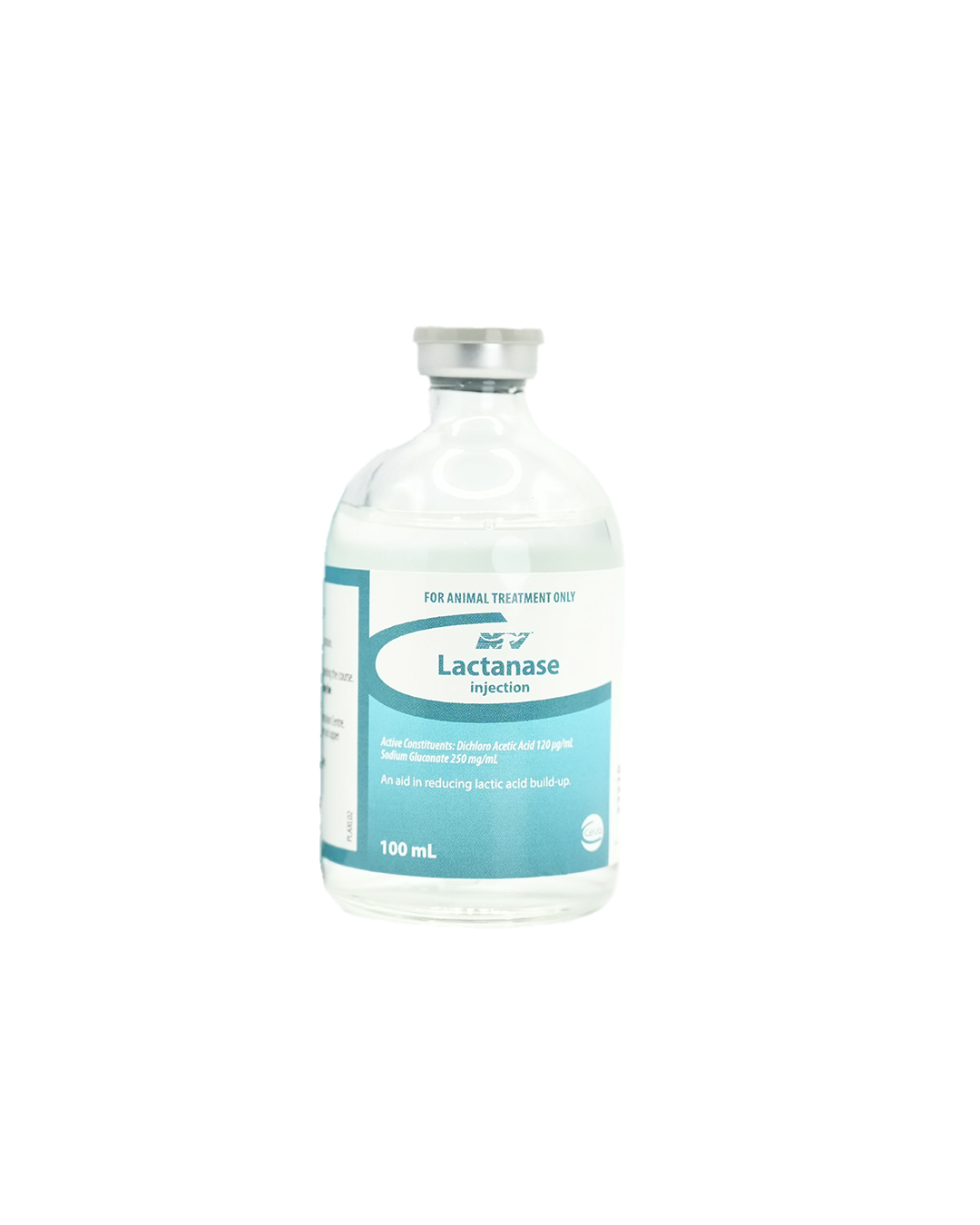
LACTANASE contains dichloroacetic acid, which is an activator of the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. This enzyme plays a central role in the process of lactic acid production during hard work. Supplementation with dichloroacetic acid (DCA) results in activation of the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase, leading to a reduction in the rate of lactic acid production and accumulation in muscles. Elevated plasma lactate levels result in a reduction in pH which contributes to muscle fatigue and decreased muscle performance.
Supplementation with DCA has been shown to reduce lactic acid accumulation during exercise, and produce a significant delay in muscle fatigue. The pathogenesis of Exertional Rhabdomyolysis (“Tying Up”) in horses is related to lactic acidosis during exercise, and associated low muscle pH. Sodium bicarbonate and dimethylglycine (DMG), which may help to reduce lactic acid accumulation during exercise, have been used to assist in the prevention of Tying Up in horses. Similarly, DCA (LACTANASE) results in a reduction in the rate of lactate accumulation, and a delay in the onset of muscle fatigue.