Description
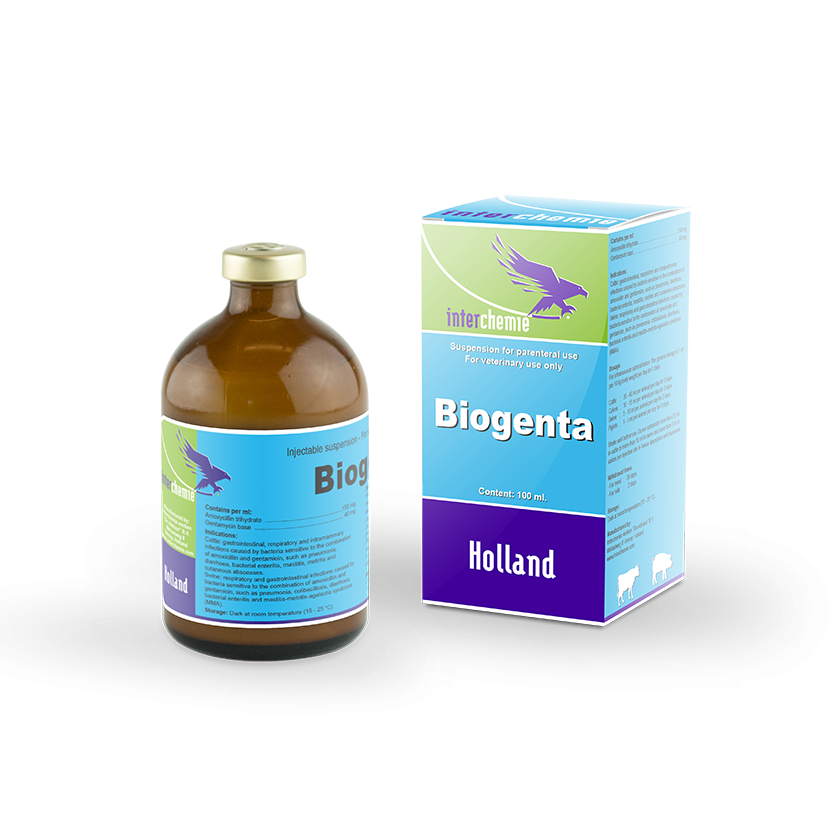
The combination of amoxycillin and gentamicin acts synergistically against a wide range of infections caused by both Gram-positive (e.g. Staphylococcus, Streptococcus and Corynebacterium spp.) and Gram-negative (e.g. E.coli, Pasteurella, Salmonella and Pseudomonas spp.) bacteria in cattle and swine. Amoxycillin inhibits mainly in Gram-positive bacteria the cross-linkage between the linear peptidoglycan polymer chains that make up a major component
of the cell wall. Gentamicin binds to the 30S subunit of the ribosome of mainly Gram-negative bacteria, thereby interrupting protein synthesis.
of the cell wall. Gentamicin binds to the 30S subunit of the ribosome of mainly Gram-negative bacteria, thereby interrupting protein synthesis.